Automatic Transmission
An automatic transmission is a sophisticated type of vehicle transmission system designed to automatically shift gear ratios as the vehicle moves, eliminating the need for the driver to manually change gears. Unlike a manual transmission, which requires the driver to engage and disengage the clutch and select gears, an automatic transmission handles all of these tasks seamlessly and efficiently, allowing for a more convenient and comfortable driving experience.
Primary Function:
The main purpose of an automatic transmission is to optimize the relationship between the engine’s power output and the rotational speed of the wheels. By automatically adjusting the gear ratio, it ensures that the engine operates efficiently under various speeds, loads, and driving conditions. This leads to smoother acceleration, better fuel efficiency, and reduced wear on engine components.
How It Works:
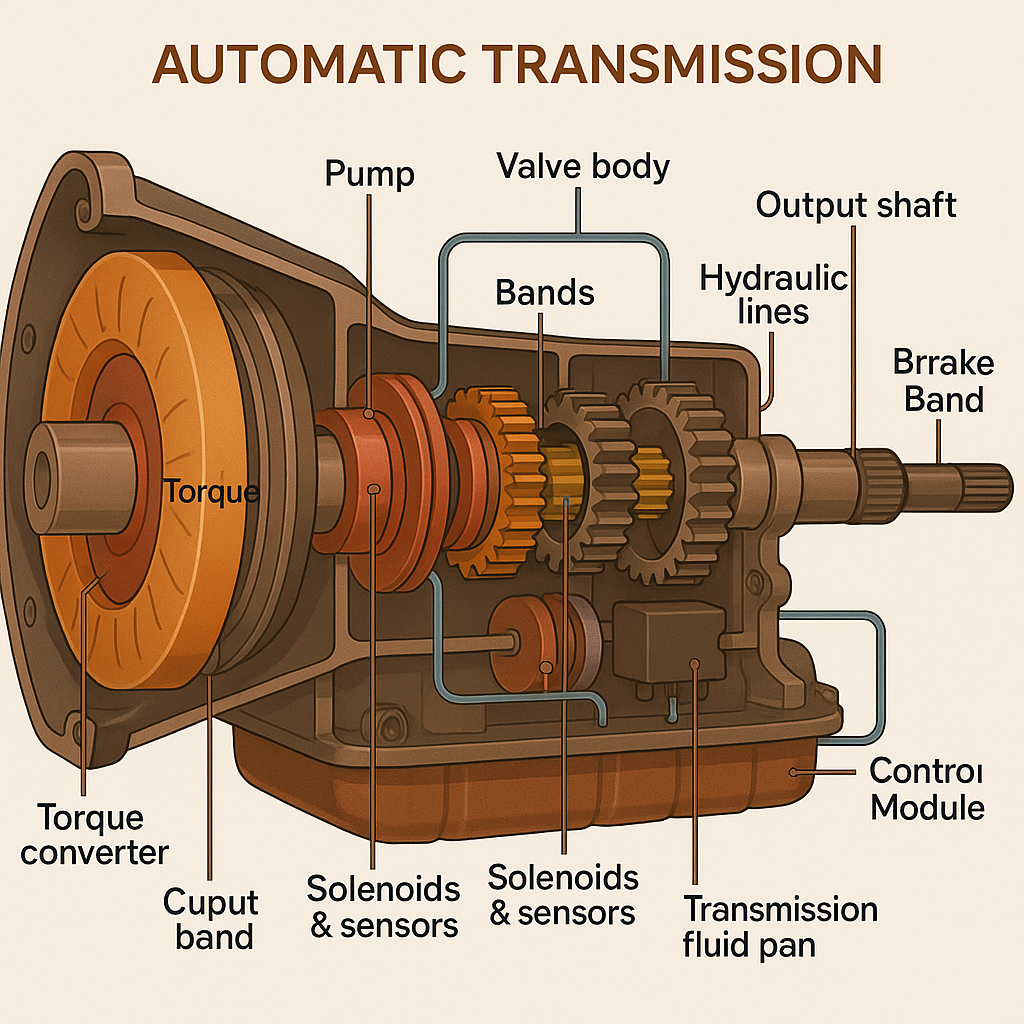
Automatic transmissions use a complex system of hydraulic controls, sensors, and computer systems to monitor driving conditions and determine the appropriate gear. Key mechanical components include:
- Torque Converter: Replaces the manual clutch. It uses fluid coupling to transmit power from the engine to the transmission, allowing the vehicle to come to a stop without stalling.
- Planetary Gear Sets: These provide the various gear ratios required for different speeds and loads. Their unique design allows for smooth shifting and multiple gear combinations within a compact space.
- Clutches and Bands: These are used to engage and disengage the different gears within the planetary sets, controlled by hydraulic or electronic signals.
- Hydraulic Valves: These direct the flow of transmission fluid to the necessary components, coordinating gear changes and ensuring smooth operation.
- Electronic Controls: Modern automatic transmissions often include computer modules that gather data from sensors (such as vehicle speed, throttle position, and engine load) to determine optimal shifting points.
Key Features:
- No Clutch Pedal: The driver only needs to operate the accelerator and brake pedals, making driving easier, especially in heavy traffic or on hilly terrain.
- Automatic Gear Changes: The transmission selects and changes gears automatically based on speed, engine load, and driving conditions, providing consistent performance.
- Standard Shift Positions: Most automatic transmissions include a gear selector with the following main positions:
- P (Park): Locks the transmission, preventing the vehicle from moving.
- R (Reverse): Engages the reverse gear for backing up.
- N (Neutral): Disconnects the engine from the wheels, allowing the vehicle to roll freely.
- D (Drive): Engages the forward gears, allowing the vehicle to move ahead and automatically shift through the gear range.
- Additional Modes: Many modern automatics also offer options such as:
- L (Low) or S (Sport): For increased engine braking or sporty driving.
- Manual Mode (+/-): Allows the driver to manually select gears for a more engaged driving experience.
Benefits:
Automatic transmissions are praised for their ease of use, making driving less stressful and more accessible. They contribute to smoother gear changes, improved comfort, and, in many cases, better fuel efficiency thanks to advancements in electronic control and gear design.
Edit By. Dr. Engineer / Adel Ramadan


thank you